The Rebus Principle
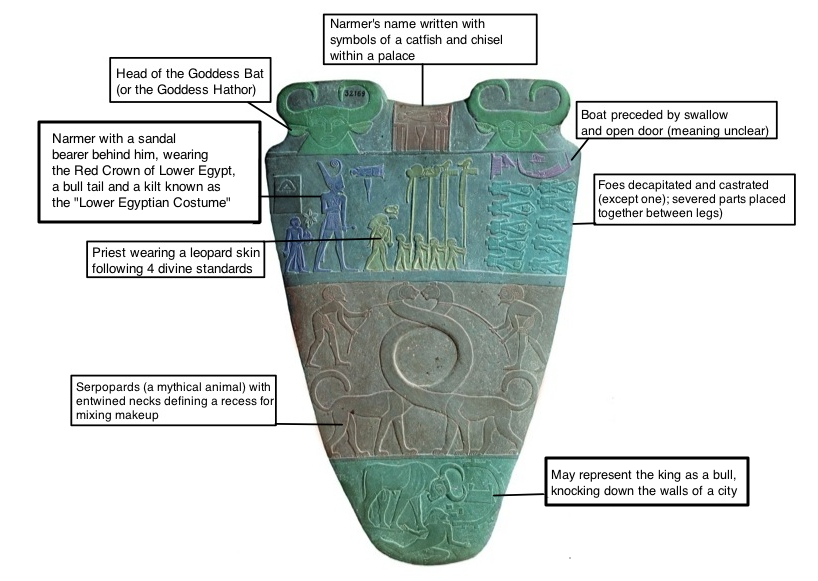
The rebus principle was applied to represent abstract words that were otherwise difficult to represent with pictograms. The rebus principle entails using existing symbols, such as pictograms, for the phonetic sound to represent new words. An early example is the Narmer Palette containing a hieroglyphic inscription, found along the Nile River in Egypt, dated around 31100 BC.
As seen in the image below, at the very top, between the two-horned heads, there is an inscription of the name Narmer. The symbol for catfish is used for the syllable “nar” and the symbol of a chisel is used for the syllable “mer.”